The Floral Transport System, a complex network within plants, plays a vital role in their reproduction and survival. It’s responsible for the movement of water, nutrients, and signaling molecules throughout the plant, enabling essential processes like photosynthesis, growth, and the development of flowers and fruits.
Understanding the Components of the Floral Transport System
The floral transport system primarily consists of two main tissue types: xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, including the flowers. Phloem, on the other hand, carries sugars produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant, including developing flowers and fruits. This intricate interplay between xylem and phloem ensures the efficient distribution of resources throughout the plant.
Xylem: The Water Highway
Xylem tissue is composed of several cell types, including tracheids and vessel elements, which form continuous tubes for water transport. These tubes provide structural support to the plant and facilitate the upward movement of water and minerals against gravity through a process called transpiration. The cohesive and adhesive properties of water molecules are crucial for this process.
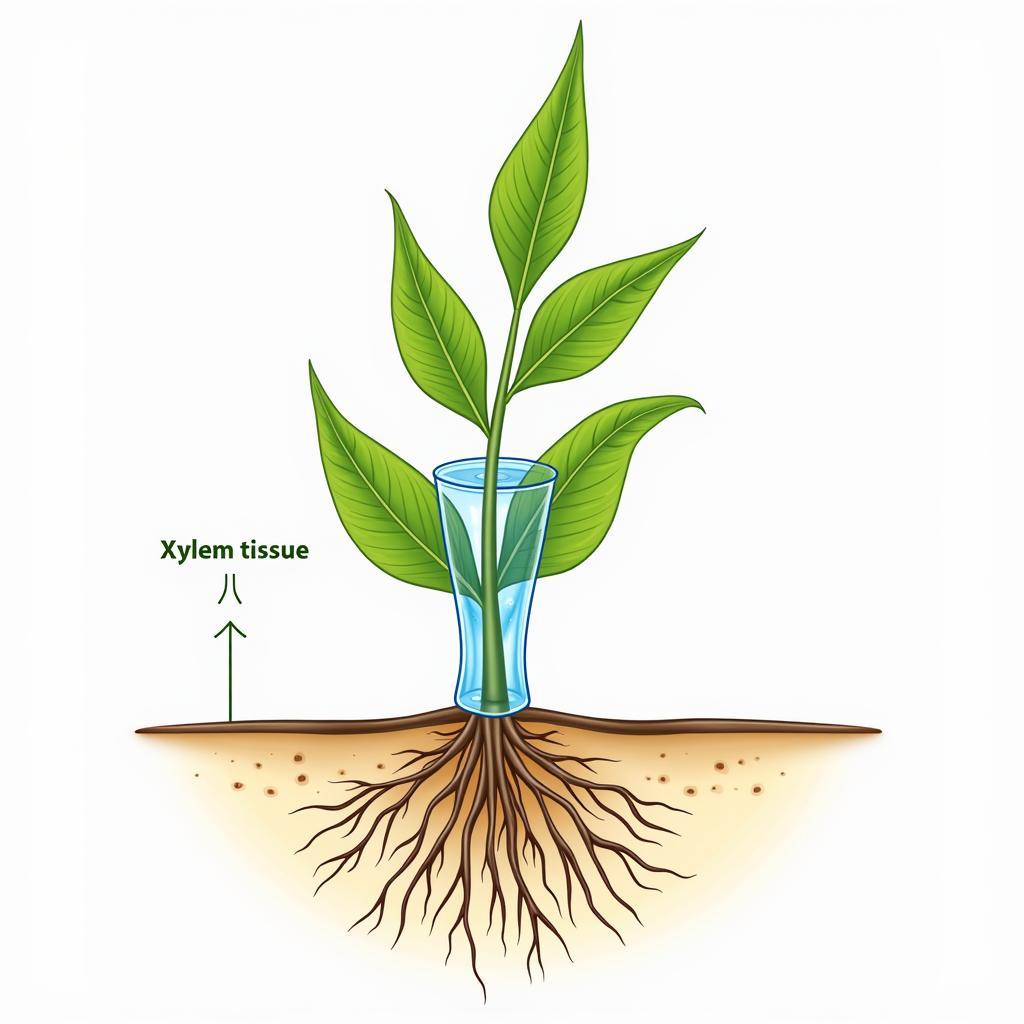 Xylem Transporting Water
Xylem Transporting Water
Phloem: The Sugar Delivery System
Phloem tissue is made up of sieve tube elements and companion cells. Sieve tube elements are living cells that form interconnected tubes for the transport of sugars. Companion cells provide metabolic support to sieve tube elements and help regulate the flow of sugars. The movement of sugars in phloem occurs through a process called translocation, driven by pressure gradients between source and sink tissues.
The Role of the Floral Transport System in Reproduction
The floral transport system is essential for various aspects of plant reproduction. It delivers water and nutrients to developing flowers, ensuring proper flower formation and maturation. It also transports sugars to developing fruits, contributing to their growth and seed development. Furthermore, the floral transport system plays a crucial role in pollen tube growth and fertilization.
Nutrient Delivery for Flower Development
The development of vibrant and healthy flowers relies heavily on the efficient delivery of nutrients via the floral transport system. Essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are transported through the xylem to the developing flower buds, promoting cell division and differentiation, leading to the formation of various floral structures like petals, sepals, and reproductive organs.
Sugar Transport for Fruit and Seed Development
After successful pollination and fertilization, the floral transport system plays a critical role in fruit and seed development. Sugars produced during photosynthesis are transported through the phloem from the leaves to the developing fruits, providing the energy and building blocks necessary for fruit growth and seed maturation.
Conclusion
The floral transport system is a vital network within plants, ensuring the efficient distribution of water, nutrients, and signaling molecules, supporting various essential processes, including growth, reproduction, and overall plant health. Understanding the intricacies of the floral transport system is crucial for appreciating the complex mechanisms that contribute to the success of flowering plants.
FAQ
- What are the main components of the floral transport system?
- How does xylem transport water?
- What is the role of phloem in plant reproduction?
- How does the floral transport system contribute to fruit development?
- What are some essential nutrients transported through xylem for flower development?
- What is translocation?
- How does the floral transport system support overall plant health?
Contact Information
For any assistance, please contact us: Phone: 0909802228, Email: doibongda@gmail.com Or visit our address: 101 Đ. Lý Chiêu Hoàng, Phường 10, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.