Lyme disease, a tick-borne illness caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, is known for its wide range of symptoms that can affect various systems in the body. While Lyme disease is primarily associated with joint pain, fatigue, and neurological issues, some individuals with Lyme disease report experiencing dental problems, leading to questions about a potential link between Lyme disease and tooth decay.
 Lyme disease symptoms and tooth decay
Lyme disease symptoms and tooth decay
Understanding Lyme Disease and Its Impact on Oral Health
While there is no direct causal relationship established between Lyme disease and tooth decay, some indirect ways Lyme disease might contribute to oral health issues exist. Lyme disease can affect the body in ways that might increase the risk of developing cavities and other dental problems.
- Dry mouth: One common symptom of Lyme disease is dry mouth, a condition that occurs when salivary glands don’t produce enough saliva. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by neutralizing acids produced by bacteria, washing away food particles, and remineralizing tooth enamel. Without sufficient saliva, the mouth becomes a more hospitable environment for bacteria to thrive, increasing the risk of plaque buildup, tooth decay, and gum disease.
- Weakened immune system: Lyme disease can suppress the immune system, making it more challenging for the body to fight off infections, including those that impact oral health. A weakened immune system might struggle to control bacterial growth in the mouth, potentially increasing the susceptibility to tooth decay and gum disease.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Lyme disease can lead to nutritional deficiencies due to digestive issues, poor appetite, or dietary restrictions. These deficiencies can weaken tooth enamel, making teeth more vulnerable to decay.
- Medications: Some medications used to treat Lyme disease, such as antibiotics, can also contribute to dry mouth as a side effect.
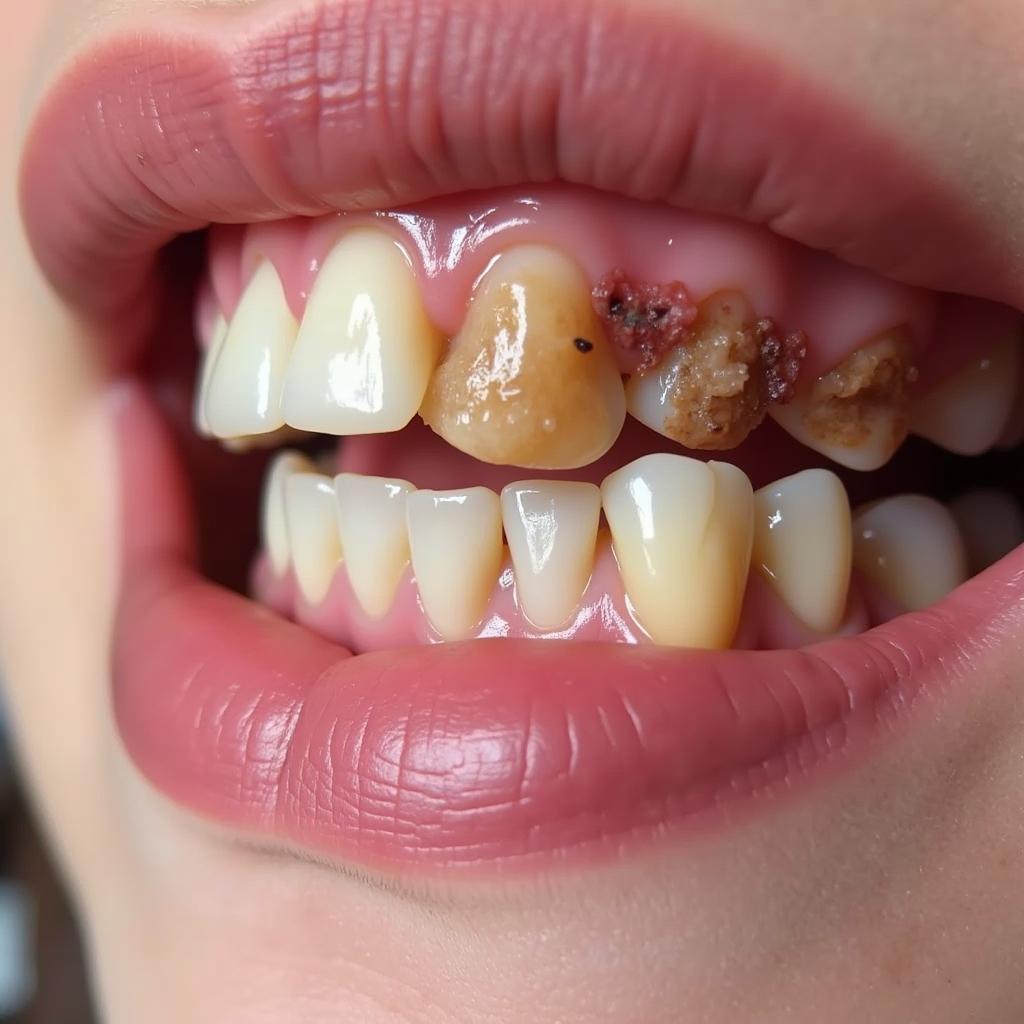 The impact of untreated Lyme disease on oral health
The impact of untreated Lyme disease on oral health
Addressing Dental Concerns in the Context of Lyme Disease
If you’re experiencing dental problems alongside other symptoms of Lyme disease, it’s essential to consult both a medical doctor and a dentist.
- Medical evaluation: Seek medical attention to diagnose and treat Lyme disease appropriately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the disease and minimize potential complications, including those affecting oral health.
- Dental checkup: Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings, especially if you’re experiencing dry mouth or other oral health concerns. Inform your dentist about your Lyme disease diagnosis so they can tailor your dental care plan accordingly.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene for Overall Health
Regardless of whether you have Lyme disease or not, maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for overall health and well-being.
- Brush and floss regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to combat dry mouth and promote saliva production.
- Eat a balanced diet: Consume a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting sugary drinks and processed foods.
- Avoid tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption: Tobacco and excessive alcohol use can negatively impact oral health, increasing the risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and other dental problems.
 Tips for maintaining good oral hygiene
Tips for maintaining good oral hygiene
By adopting a proactive approach to oral health and seeking appropriate medical and dental care, you can mitigate potential risks and maintain a healthy smile.