Lyme disease, a tick-borne illness caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, is known for its wide range of symptoms that can affect various systems in the body. While joint pain, fatigue, and neurological issues are commonly associated with Lyme disease, some individuals report experiencing dental problems, including tooth loss. This raises the question: could there be a connection between Lyme disease and losing teeth?
Understanding Lyme Disease and Its Impact on the Body
When an infected tick bites a person, the bacteria enter the bloodstream and can spread to different parts of the body, including the nervous system, heart, and joints. The immune system responds to the infection, but the inflammatory response triggered by the bacteria can also contribute to tissue damage.
 Lyme disease bacteria spreading through the bloodstream
Lyme disease bacteria spreading through the bloodstream
Could Lyme Disease Affect Oral Health?
While there is no direct evidence that Lyme disease directly causes tooth loss, some indirect mechanisms could contribute to oral health issues in individuals with the disease:
- Inflammation: Lyme disease triggers inflammation throughout the body, and this inflammation could potentially affect the gums and tissues supporting the teeth, leading to periodontal disease. Periodontal disease, if left untreated, can weaken the gums and bone, eventually resulting in tooth loss.
- Immune System Dysregulation: Lyme disease can disrupt the immune system’s normal function, making it difficult for the body to fight off infections effectively. This could make individuals with Lyme disease more susceptible to oral infections like gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Chronic Lyme disease can interfere with nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies that impact overall health, including oral health. For instance, deficiencies in vitamin D and calcium can weaken bones, including the jawbone, increasing the risk of tooth loss.
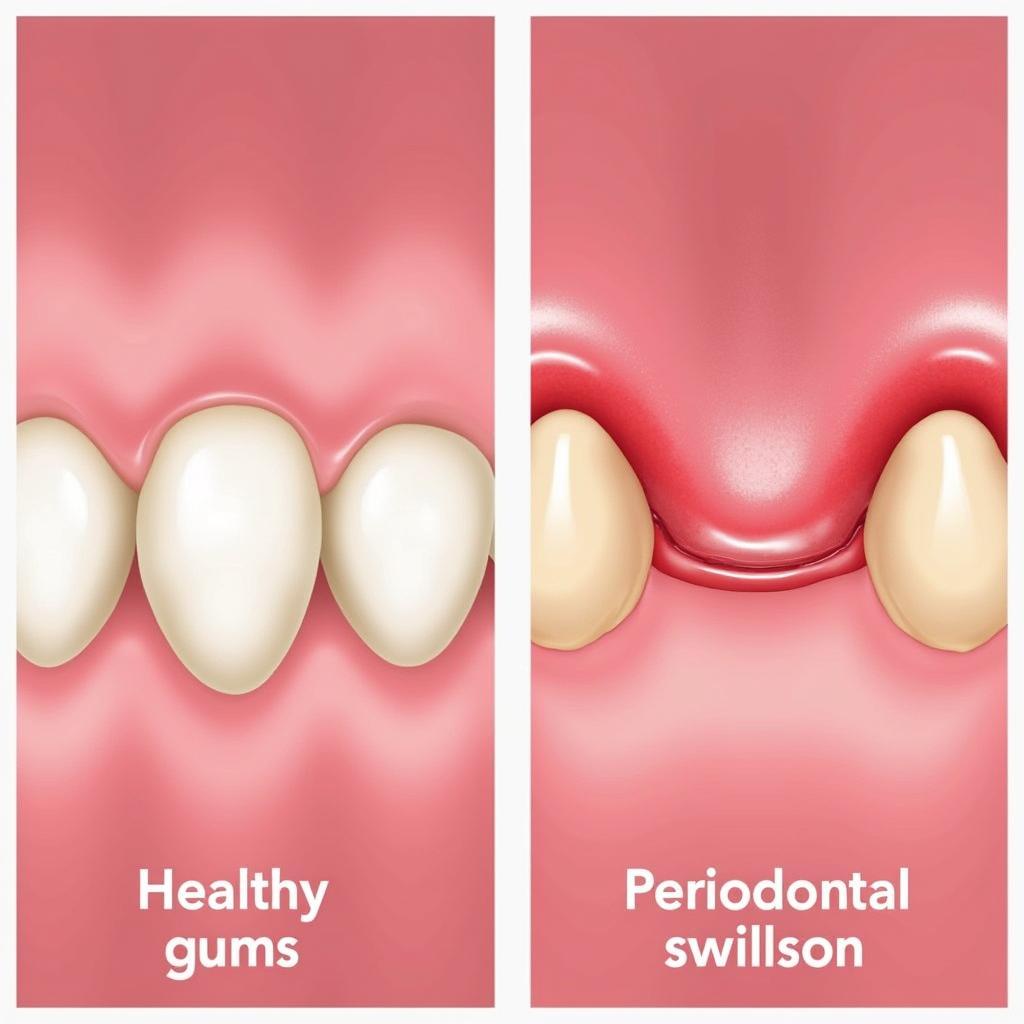 Healthy gums vs. gums affected by periodontal disease
Healthy gums vs. gums affected by periodontal disease
Recognizing the Signs and Seeking Professional Help
It’s crucial to remember that experiencing dental problems does not necessarily mean someone has Lyme disease. Many other factors can contribute to oral health issues. However, it’s essential to be aware of the potential indirect link between Lyme disease and dental problems, especially for individuals diagnosed with the illness or living in areas where Lyme disease is prevalent.
If you have Lyme disease and are concerned about your oral health, it’s crucial to consult with both a medical doctor specializing in Lyme disease and a dentist. Early detection and treatment of both Lyme disease and any dental issues are essential for preventing potential complications.
Lyme Disease and Dental Health: Addressing Common Questions
Can Lyme disease cause dry mouth?
While not a direct symptom of Lyme disease, some individuals may experience dry mouth as a side effect of medications used to treat the illness.
Is there a specific test to determine if dental problems are related to Lyme disease?
No, there is no specific test to determine a direct causal relationship between Lyme disease and dental issues. Diagnosis involves assessing overall health history, dental examination, and ruling out other potential causes.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene for Overall Health
Regardless of Lyme disease, maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for overall well-being. Brushing twice a day, flossing daily, eating a balanced diet, and visiting the dentist regularly can help prevent dental problems and ensure a healthy smile.
Remember, while Lyme disease can impact various aspects of health, maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals is crucial for addressing concerns and receiving appropriate care. If you have any questions or need assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us at Phone Number: 0909802228, Email: doibongda@gmail.com, or visit us at 101 Đ. Lý Chiêu Hoàng, Phường 10, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh, Việt Nam. Our dedicated team is available 24/7 to provide support and guidance.